Table of Contents
Calling all the sea adventure freaks! What do you need the most for a wild trip over the blue waters? Yes. A fit, shiny, waxed-up, and polished boat to ride on. If you’re an outdoor trip enthusiast, you must know all the know-how and what exactly gets your boat going. You must have the idea of the stern or cockpit of the boat. However, do you know what is the widest point of your sea cruiser? What is the back of the boat called? A boat transom. One of the admirable things about this transom is that it not only increases the look of your vessel but also ensures you have a secure grip on the wide seas.
What exactly does this thing work, if you must be thinking? Well, what are we here for? Hence, let us explore all this and much more on this journey towards the bluest seas ever!
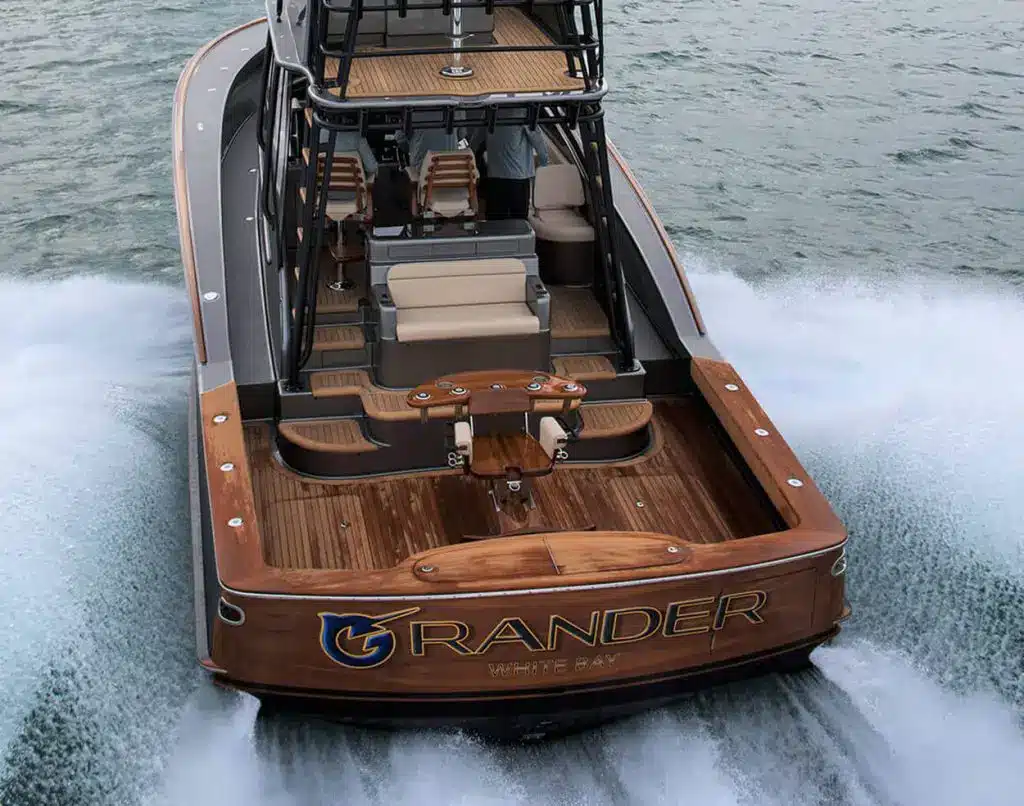

What is a Boat Transom?
Learning about the parts of the boat before taking it out on a crazy sea adventure is necessary. Whether it’s that hatch, stern, or the cockpit, it is always important to know about your boat. Now, you must be wondering what actually a boat transom is.
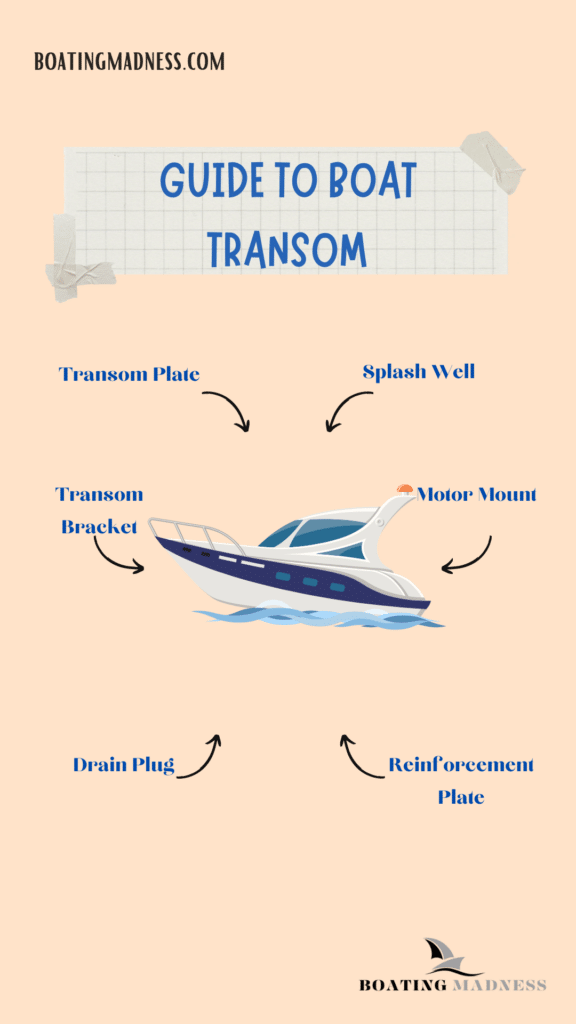
- The transom is a vertical reinforcement at the rear of the boat. It divides the upper section of the stern and is one of its widest points opposite to the lowest point.
- In addition to supporting the outboard motor, the transom may have metal fittings, windows, and lighting. It is crucial for the security of boats.
- The transom, seen on many vessels, including sailboats, can feature windows or French doors opened and closed for air conditioning and natural light.
It’s essential to understand what a boat’s transom is and where it is located. Hence, the stern is the area behind the ship, which is the opposite of the bow. Boating safely and effectively is ensured by knowing these components. Therefore, one cannot stress the importance of the transom in boating. Let us learn some tips on how to use this transom on your sailboat.
A Guide to Using the Transom
The boat transom is essential to your boat’s design, fortifying the aft and part of the stern. Therefore, understanding its purposes and functioning will improve your boating experience. So, this is a thorough tutorial on using the transom effectively.
Bolstering the Boat with Reinforced Material
- Fiberglass reinforcement is used to create modern transoms.
- This material resists deterioration from other substances and seawater.
- It is durable since it can sustain the weight of extra goods.
Engine Assistance
- Outboard motors are installed on the transoms of the majority of personal watercraft.
- These transoms are specifically made to be mounted on engines.
- Motors can be raised using a motorized method or submerged permanently.
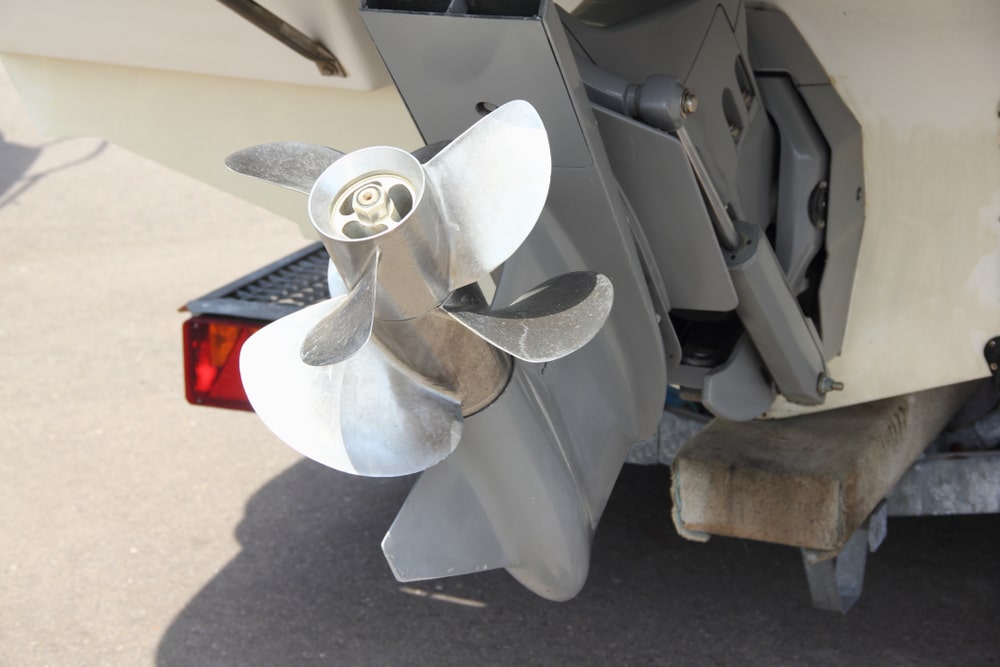

Additional Fixtures of a Boat Transom
Here’s a look at some of the additional features of your boat transom.
Flexible Style
- Additional fixtures in boat transom like consoles, rear or front doors, and ladders are frequently seen on transoms.
- Hence, these fixtures will make your yacht more convenient and functional.
Sturdiness and Absorption of Force with Boat Transom
Let’s understand a bit about the engine dispersion force.
Engine Dispersion Force
- Boat transoms are strong and can support a large amount of engine force.
- Powerboats use a transom to transfer engine power to the hull.
- The boat transom’s broad design aids in the safe dispersal of kinetic energy.
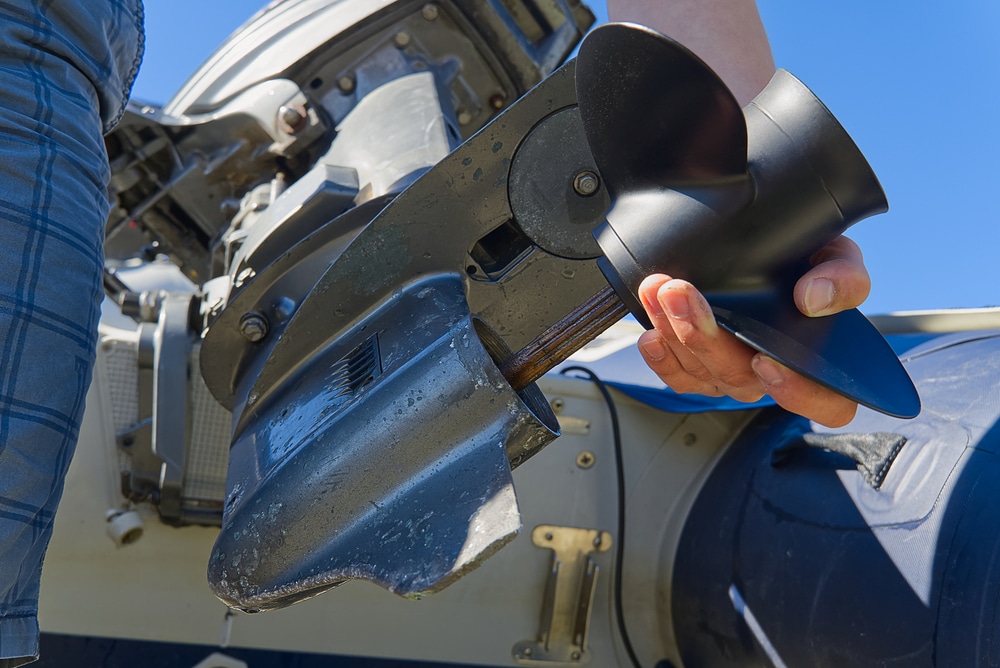

Taking Care of Your Boat Transom
Now, how can you take care of your boar? Let’s explore.
Continual Examination of Boat Transom
- Examine Following Each Usage: Carefully check your boat transom for wear or damage after each voyage.
- Seek for Leaks and Fractures: Examine the seals surrounding nuts, screws, and fittings for any cracks, leaks, or peeling.
Hence, examine the transom for signs of moisture, such as mushy spots or discolored regions, which could indicate that it is wet.
Recognizing Possible Problems
- Test by Knocking: Tap on the boat transom to perform a knock test. A hollow sound may indicate potential rot.
- Look for Any Signs of Rust: Rust marks near nuts and screws indicate possible decay and water penetration.
- Examine the Area for Warping and Cracks: Surface cracks or noticeable warping are telltale signs of transom deterioration in a boat transom.

Preventive Actions
- Sealant Upkeep: To stop water from seeping in a boat transom, make sure all seals around nuts, screws, and fittings are intact, and reapply sealant as needed.
- Maintain Snug Fittings: To preserve structural integrity, tighten nuts and screws regularly.
- Employ High-quality Materials: When changing or repairing parts, utilize marine-grade materials meant for extended immersion in water.
Expert Assessment
- Speak with an Expert: If you think there may be a leak or substantial damage in your boat transom, get a professional evaluation to determine the degree of any problems.
- Rot Detection: Experts can precisely perform tests to identify rot or dampness on boat transoms.
A Glimpse into the Material Used for Boat Transoms
Boat transoms are essential structural components that stabilize the stern of the boat and support the mounting of outboard engines. Hence, boat ransom material selection varies according to type of boat, intended use, and required durability.
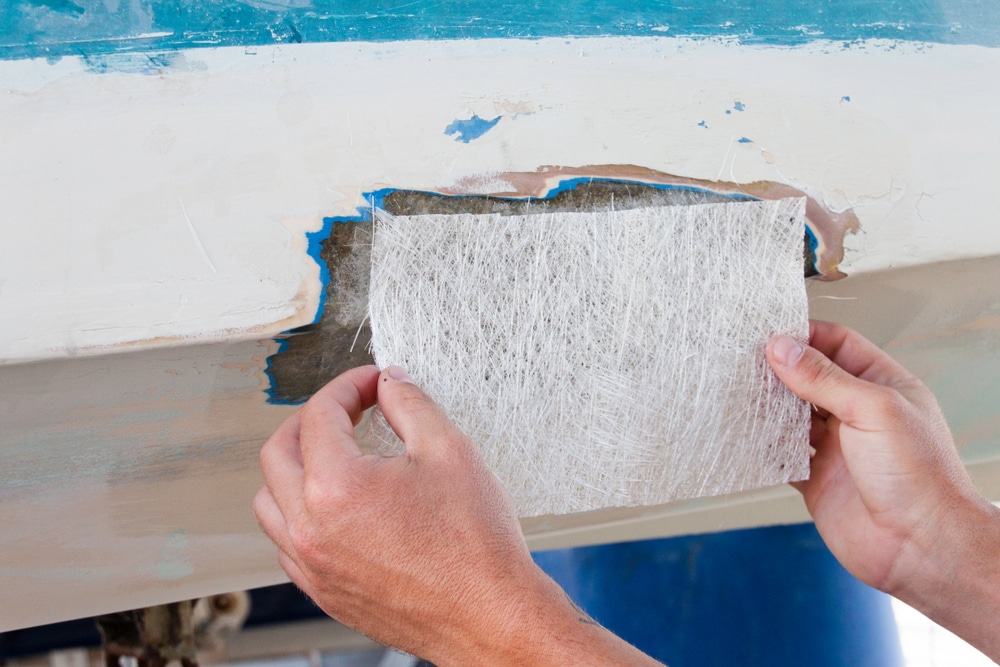

1. Material Composition of Fiberglass Boat Transoms
Generally, layers of resin-impregnated fabric are used to make fiberglass boat transoms. This composite material is very strong and durable.
Benefits
- Strength: Fiberglass has a well-known high strength-to-weight ratio, which makes it perfect for solid transoms that can withstand heavy loads from outboard engines.
- Durability: Fiberglass transoms require less maintenance than their wooden counterparts because they resist decay and corrosion.
Taking into Account
- Water Intrusion: Fiberglass boat transoms are durable, but problems may arise if they are not adequately sealed.
- Therefore, over time, water intrusion can cause delamination and potentially jeopardize the core material, which is frequently plywood.
2. Material Composition of Aluminum Boat Transoms
Secondly, aluminum transoms are made from marine-grade aluminum alloys, which are strong and lightweight.
Benefits
- Lightweight: Aluminum boat transoms improve performance and fuel efficiency by reducing the boat’s overall weight.
- Corrosion Resistance: In marine conditions, aluminum’s inherent ability to develop a protective oxide coating reduces its susceptibility to corrosion.
Taking into Account
- Galvanic Corrosion: Aluminum transoms are susceptible to galvanic corrosion when they come into contact with different metals or under specific circumstances.
- Appropriate coatings and isolation reduce this risk.

3. Material Composition of Wooden Transoms
Next, the Marine-grade plywood is typically there to construct wooden boat transom, frequently layered for strength.
Benefits
- Traditional Appeal: Due to their timeless design and ease of maintenance, wooden boat transom are a choice.
- Flexibility: Wood is bendable and repaired quite simply when in comparison to metals or composites.
Taking into Account
- Rot and Decay: Wooden boat transom is prone to rot and decay when exposed to moisture if not sealed and maintained correctly. Make sure you own a nice cover for your boat protection and safety.
- Weight: The larger weight of wooden transoms compared to their composite or aluminum counterparts on the left side can impact a boat’s total weight and performance.

Final Thoughts
Summing up, navigating the boating world requires a solid understanding of your vessel’s transom, the crucial cross section at the stern. The widest point on a boat that divides the upper section of the stern, known as the transom, supports the outboard motor and improves boating safety. Therefore, it is necessary to mount engines, transom lights, and window or door to allow air conditioning and natural light. The boat’s integrity depends on the transom, whether on a sailboat or any other vessel.
In conclusion, understanding a back of the boat aka the boat’s transom makes recognizing essential components, such as this part of the boat is called the bow, easier and guarantees smooth sailing. Hence, a strong transom keeps every element of the ship, including the metal fittings and transom windows, safe and separates the top to the bottom.
Have a crazy sailing adventure!